Nutrition
An excellent article from Sujata Gupta in the journal Nature discusses what happened when we started eating meat, and what happens when we don’t eat it. Key takeaways include:
- To build and maintain a more complex brain, our ancestors used ingredients found primarily in meat, including iron, zinc, vitamin B12 and fatty acids.
- Deficiencies in the micronutrients found in meat have been linked with brain-related disorders, including low IQ, autism, depression and dementia.
- Compared with the other groups, students in the meat group had greater muscle mass and fewer health problems…Cognitive performance was stronger, too.

Evidence from Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention has found a correlation between high-glycemic diets and lung cancer. To which you’re probably thinking, “I thought you could only get that from smoking?” Well, unfortunately that’s not the case, and the researchers found twice the risk in those with the highest GI diet compared to those with the lowest. But that being said, it was an epidemiological study based on self-reported food surveys; so take it with a grain of salt.
The review studies looking at a Mediterranean and heart disease may be too good to be true, according to this study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. The researchers evaluated systematic reviews and meta-analysis’ over the last decade and concluded that the current available evidence is of extremely low quality.
A new study reiterates what anyone following Live It NOT Diet! now understands – eating more protein increases fullness. Prior to this in-depth meta-analysis there wasn’t a conglomerate of evidence, so this one’s good to bookmark! Not surprisingly, there was also a study this month showing that a higher-protein (1.5g/kg vs 0.8g/kg) intake improves sleep quality during weight loss. The subjects were calorie restricted, which we’re not about, but it does show that protein alone can make all the difference in the world with respect to your success rate.
Research in the journal Circulation used blood collected from two prospective cohort studies (the Nurse’s Health Study and Health-Professionals Follow-Up Study) to identify an association between higher dairy fat in the blood and a lower risk of diabetes.
We’ve talked in great length on the importance of animal products, and a study in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association builds on that by discussing the negative consequences of a vegan diet. Not only highlighting the nutrient deficiencies – B-12, iron, vitamin D, protein and omega-3 fatty acids – but reviewing the future health issues.
Speaking of future health issues, new evidence in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution highlights the genetic changes that occur over-time in populations relying on a vegetarian diet. The good news is, the lifelong vegetarian subjects tested experienced a genetic adaptation that enhances their ability to synthesis essential fatty-acids from plant-based foods. The bad news is, this mutation (rs66698963 found in the FADS2 gene) exposes them to chronic inflammation and the diseases that accompany it (heart disease, cancer, etc). Since the plant oils are easily converted to the pro-inflammatory arachidonic acid, without the accompanying DHA/EPA – discussed here.
Fitness
If you enjoy dancing as your form of low-intensity activity, go ahead and keep doing it. As this study from the American Heart Association looked at Latino dancing specifically, and saw improvements in walking performance, and an increase in leisure activity (outside of dancing) by nearly 200 minutes.
Time to ditch the car? Aside from the convenience of services like UBER, that are starting to make you question your vehicle, the evidence for walking, cycling, and even taking public transit to work continues to grow. For instance, this study from The Lancet showed significantly lower weight and BMIs in non-car commuters, with cycling showing the greatest difference at 11lbs (1.71 BMI) for men and 9.7lbs (1.65 BMI) for women.

Evidence continues to mount that daily physical activity is one of the best ways to lower your risk of Alzheimer’s and dementia. With research in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease showing larger brain volumes with greater activity levels, and a 50% reduction in risk (25% in those already impaired).
It’s been suggested in the past that over-specialization in a sport can have negative repercussions, and this observational study in the American Journal of Sports Medicine adds to it. Showing that high-school athletes participating in a single-sport for more than 8 months per year were more likely to experience knee and hip injuries. What’s the take-home? Variety and anatomical balance (front to back, left to right, upper to lower) is the key to injury prevention and optimal performance; whether you’re an athlete or not.
A new study in the Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research demonstrates the negative impact endurance training has on strength development. With individuals splitting their time between cardio and weight-lifting (1:1) developing less strength over 6 weeks than their weight-lifting only (3:0) and predominantly weight-lifting (3:1) counterparts. Not surprisingly, they also had noticeably higher levels of cortisol.
Lifestyle
Exposure to Lead appears to cause a shift in gut bacteria that could negatively affect future health and body composition. Researchers in the journal Toxicological Sciences added reasonable amounts of lead (similar to what human exposure) to the drinking water of mice and saw altered gut microbiota in both sexes, and increased bodyweight in males.
Brown fat is the ‘good’ energy producing kind that is elevated during exercise, fasting, and cold thermogenesis (shower, weather, etc). According to new research in the journal Cell Metabolism, one of the reasons high brown fat levels may be so beneficial is because they need to feed on glucose to produce heat. And interestingly, it follows a circadian rhythm where it’s stimulated first thing in the morning.
Occupations that revolve around sitting are a major cause for concern according to a pilot study in the journal Preventive Medicine Reports. The research focused on bus drivers, who spend upwards of 83% of their workday sitting and 68% of their non-working day sitting. Resulting in high body fat %’s and an extremely poor cardiometabolic profile.
It appears people are healthier in retirement because they sit less (-68min/day), move more (+93min/week) and sleep better (+11min/day). Now the tough part – convincing people they don’t have to retire to do this.

This may help! Just 30 minutes of lost sleep per night results in a 17% increased risk in obesity and 39% increased risk of insulin resistance. With researchers from Weill Cornell Medical College also finding that those with a sleep debt were 72% more likely to be obese compared to those without.
Elevated cortisol levels are a normal occurrence during pregnancy, but research from the American Psychological Association shows that excessive levels usually result in an underweight baby. So, ditch the chronic cardio, avoid inflammatory foods, and make sure you’re sleeping well.
More evidence that light exposure in the day is just as important as darkness in the evening. With this study finding that mice exposed to bright-light in the daytime were better able to avoid the melatonin-suppressing affects of light exposure at night.
Health & Disease
An interesting opinion piece in JAMA Oncology discusses the harsh reality that cancer can only be defeated with prevention; regardless of the resources and enthusiasm the government continues to put towards a cure.
“…indeed, there have been some important and notable cures for certain types of cancer over the last 45 years…However, these are responsible for only a small fraction of this improvement in mortality.”
Your child’s behaviour could have a lot to do with their hormone levels, according to new research in the American Journal of Human Biology. The study tested 90 primary school children, and found an increase in aggressive behaviour in boys whose cortisol (stress) levels rose between the ages of 8 and 10, and decreases with elevations in estradiol (i.e. estrogen).
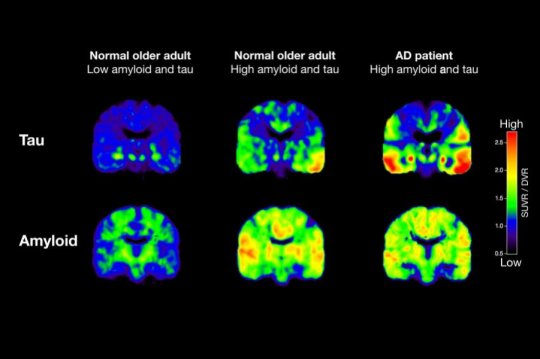
Researchers from the University of California present PET scans in the journal Neuron, to show the overload of beta-amyloid and tau that occurs in Alzheimer’s patients. The scientists still aren’t sure what comes first – the excess tau or the excess beta-amyloid – but both are a clear sign of cognitive dysfunction. And as my friend Amy Berger lays out in The Alzheimer’s Antidote, both are preventable!
Lots of evidence surfacing that ties skin conditions, like rosacea, to neurological disorders, like Parkinson’s Disease (1, 2). Yes, it’s observational research, but based on the fact that both conditions are pretty obvious, and both are chronic-inflammatory conditions, it shouldn’t come as a surprise. If you’re dealing with a skin condition, like acne, eczema, rosacea, psoriasis, take a look at this, this, and this; which should help connect the dots on the underlying cause.
Questions always arise regarding whether organic pesticide-free food and expensive all-natural cleaners and beauty products are really worth it. Which is usually a tough conversation for people that think it’s all pseudo-science, or are unwilling to part with a few extra dollars. But that’s until research like this comes out. Not only showing that endocrine-disrupting chemicals (like DDT and phthalates) exist, and they contribute to significant reproductive problems (tumors, fibroids, endometriosis, infertility, birth defects, etc), but that the health care costs are SIGNIFICANT. With this specific study in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism linking it to 1.4 billion for the European Union.
Medication & Supplementation
Children born to vitamin-D deficient mothers are 90% more likely to develop Multiple Sclerosis as an adult. Levels under 12.02ng/mL were considered deficient.
No shocker here, but fish oil seems to have no impact on your ability to gain muscle – at least when looking at a group that’s lifting weights and consuming whey protein. The researchers had 20 healthy males consume either fish oil or coconut oil prior to resistance training for 8 weeks, and saw no marked difference in MPS (muscle protein synthesis).
Antibiotic use before age 2 may increase risk of childhood obesity at 4 years of age, according to new evidence from the American Gastroenterological Association. The absolute risk was only 1.2%, and the relative risk of 25% could be the result of higher obesity rates overall, but based on what we know about gut bacteria and body composition, this wouldn’t be surprising.

Stay Lean!
Coach Mike
RELATED ARTICLES:
Are You Eating Enough Protein?
Cardio - The Worst Investment Ever
How Poor Sleep Makes You Fat & Sick
